Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) combines acceptance and mindfulness strategies with behavior-change tactics to help individuals increase psychological flexibility (a.k.a. mental and emotional resilience). If you’re considering ACT therapy in a professional setting, you likely have many questions about how to find an ACT therapist, such as what to look for in a therapist, what to expect from sessions, how much therapy would cost, and more. Well, we’ve got you! Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate this process.
What Are the Steps in ACT Therapy?
ACT therapy is organized around six core processes (a.k.a. ACT Hexaflex model) that help guide clients toward greater psychological flexibility. Here are the steps involved in a nutshell:
Acceptance involves opening up to and accepting unwanted thoughts and feelings instead of denying, fighting, or avoiding them. With this skill, you’ll learn to acknowledge the presence of discomfort without letting it dictate your behavior.
Mindfulness (Present-Moment Awareness) emphasizes being fully engaged in the present moment. Mindfulness helps you shift your focus from worrying about the past or future to becoming more aware of your current experiences.
Cognitive Defusion is the practice of detaching yourself from unhelpful thoughts and viewing them more objectively. It helps you reduce the influence of negative self-talk and limiting beliefs.
Self-as-Context encourages you to view yourself from a broader perspective. Instead of identifying solely with your thoughts, emotions, or experiences, you learn to see yourself as the observer of these experiences.
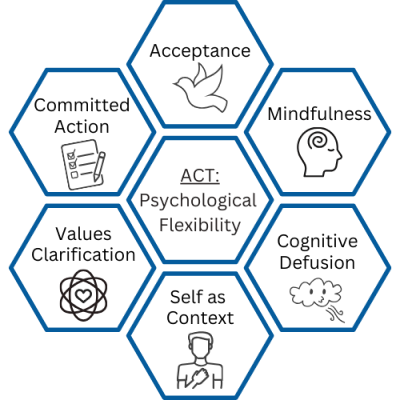
Values Clarification is the practice of exploring and defining one’s core values. According to ACT, a mismatch between our core values and how we live (our daily actions, lifestyle, etc.) is one of the roots of unhappiness and unfulfillment in life. So, to truly live the life you want, you must first identify what truly matters to you.
Committed Action emphasizes taking practical steps toward goals that align with your values. This may involve behavior changes, goal setting, and adopting new habits.
How Many ACT Therapy Sessions Do You Need?
Since there are various processes involved, you can imagine that the duration of ACT therapy can vary depending on your needs and goals. While some individuals might experience significant improvements in just a few sessions, others may benefit from longer-term therapy.
However, in general, ACT is considered a shorter-term approach and can last anywhere from 8 to 16 sessions, with each session lasting an hour. Just keep in mind that the length ultimately depends on the complexity of the issues you want to address. Here are some general guidelines.
- Short-Term Therapy. For specific, targeted issues (like a phobia or workplace anxiety), ACT therapy may last around 6-12 sessions.
- Medium-Term Therapy. If you’re seeking help for moderate anxiety, depression, or life transitions, you might expect 12-20 sessions.
- Long-Term Therapy. More complex challenges, such as chronic trauma or deeply rooted behaviors, may require 20 or more sessions over an extended period.
Keep in mind that the above is just a guide. Ultimately, your ACT therapist will collaborate with you to create a personalized treatment plan based on your needs.
What to Expect During a Session
ACT therapy is structured yet flexible. Considering its six core processes, here’s what you can typically expect during sessions.
- Getting to Know You / Rapport Building. It’s very important to feel that the therapist is genuinely interested in who you are and really wants to help you. During your initial sessions, pay attention to whether they actively listen, show empathy, and create a safe and comfortable space for you to share. If it feels like they’re truly trying to understand you, that’s a great sign. Building a strong connection makes a huge difference in how therapy works for you!
- Acceptance Strategies. Acceptance is at the core of ACT, so expect to learn strategies that will help you make room for uncomfortable situations, thoughts, and emotions (instead of trying to fight or avoid them).
- Mindfulness Exercises. ACT therapists will guide you through various mindfulness practices to increase your awareness of the present moment. These practices help you observe thoughts and emotions—without judgment.
- Cognitive Defusion Techniques. Instead of trying to change negative thoughts, you’ll work on altering your relationship with them. For example, you may label thoughts as simply “thoughts” rather than facts.
- Values Exploration. Your therapist will help you identify what truly matters to you in life. By clarifying your values, you can set meaningful goals that align with them.
- Committed Action (Goal Setting + Planning). Sessions may involve discussing practical steps you can take to move toward a more meaningful, values-driven life.
- Experiential Exercises and Homework. ACT therapy often extends beyond the therapy room. You might receive assignments or tasks to practice in daily life, reinforcing what you’ve worked on during your sessions.
How to Find an ACT Therapist Near You
Now that you know more about ACT and what to expect during a therapy session, here are some key steps to consider to find an ACT therapist.
Search Reputable Databases.
- Psychology Today and GoodTherapy offer directories where you can filter therapists by location and specialty, including ACT.
- The Association for Contextual Behavioral Science (ACBS) maintains a directory of certified ACT therapists worldwide.
Check Credentials and Training.
- Look for a therapist with specialized training in ACT. Many professionals undergo post-graduate training, workshops, or certification programs in ACT.
- Ensure the therapist holds appropriate licenses or certifications in their area of expertise (e.g., licensed clinical psychologist, licensed professional counselor).
Experience. Experience. Experience.
- When you find a potential therapist, inquire about their experience using ACT. Ask how long they have practiced this approach and with which specific conditions they have the most experience.
VERY IMPORTANT: Consider Personal Fit.
- Therapy works best when you feel comfortable and understood by your therapist. Consider scheduling an initial consultation to gauge if their approach resonates with you.
Seek Recommendations.
- Ask friends, healthcare providers, or online communities for recommendations.
Real-Talk: Many people today find that therapy doesn’t work for them. (Just look at Reddit groups, and you’ll know what I mean.) So, here’s my tip: On your first session, whether that’s a consultation session or not, mention your goals or what you want to get out of therapy. Even if you’re unsure, even if you think that what you have in mind is vague, mention it anyway and then ask the therapist about how they plan to help you get from Point A to B. Depending on their reply, ask yourself if this is a therapist you want to work with.
How Much Does an ACT Therapy Session Cost?
The cost of ACT therapy varies based on location, therapist experience, and the type of therapy provided (individual, group, etc.). Here’s a general overview.
- Average Costs. In the U.S., therapy sessions typically range from $100 to $250 per hour, though prices can vary widely depending on the therapist’s credentials and location. In other regions, prices may be higher or lower.
- Insurance Coverage. Check if your insurance plan covers mental health services, including ACT therapy. Many providers cover a portion of therapy costs, reducing your out-of-pocket expenses.
- Sliding Scale Fees. Some therapists offer sliding scale fees based on income, making therapy more accessible for those with financial constraints.
- Group Therapy Rates. Group ACT therapy sessions may be more affordable, usually ranging from $40 to $100 per session.
Important: Discuss fees and payment options during your initial consultation to ensure you can make informed decisions about your therapy.
ACT Therapy at Home: An Affordable Alternative
Understandably, for many people, the cost of therapy is a concern. Fortunately, there are ways to practice ACT at home. While working with a professional therapist can offer personalized and professional guidance, self-help methods are more cost-effective for those on a budget. Here are some options to explore:
Self-Help Books and Workbooks. ACT-based books and workbooks can help you understand ACT processes and how to apply them in your daily life. These resources often provide step-by-step instructions, examples, and worksheets or activities you can try from the comforts of your own home.
Sel-Help Resources on Amazon:
The ACT Therapy Workbook for Adults
The ACT Therapy Workbook for Anxiety Relief
Online Courses and Apps. Several platforms offer online ACT courses, interactive modules, and exercises that you can work on at your own pace. Apps designed for mindfulness and ACT practices, such as guided meditation and acceptance exercises, can be a helpful addition to your routine.
ACT Exercises and Worksheets. If you already have a basic understanding of ACT, then perhaps you want to try free worksheets online that focus on the six core processes of ACT. Completing these exercises can help reinforce ACT principles in your daily life.
Support Groups. Look for community or online support groups that focus on ACT principles. Engaging in group discussions and sharing experiences with others can provide motivation and insight as you apply ACT techniques at home.
Note: Self-guided ACT or ACT therapy at home can provide valuable insights and strategies. However, for individuals dealing with severe mental health issues, complex trauma, or those who find it challenging to self-motivate and implement techniques independently, professional support is often essential for effective progress and healing.
How Do You Know if ACT Therapy Sessions Are Working?
Short answer: If you’re starting to feel better.
Long answer: You’ll know ACT therapy is working when you start noticing meaningful changes in your everyday life. Here are some key signs:
- Increased Awareness: You become more present and aware of your thoughts and feelings instead of feeling caught off-guard or overwhelmed by them.
- Less Avoidance: You find yourself more willing to face challenges and uncomfortable situations head-on.
- Living by Your Values: You feel more aligned with what truly matters to you, making decisions based on your values, even when it’s uncomfortable or hard.
- Greater Flexibility with Thoughts: Negative thoughts or worries may still show up, but they don’t control you anymore. That is, they no longer dictate your behavior as strongly. You learn to see thoughts as just thoughts rather than facts you must act on.
- Sense of Progress: Overall, you feel more open to life’s ups and downs, handle stress better, and notice growth in your emotional resilience.
Important: Hey, everyone’s journey is different. So, as long as you feel like you’re moving forward, take it as nothing short of progress! Also, be open with your therapist. For example, suppose you feel that you’re making progress on one ACT core skill (e.g., Mindfulness) but not on others (e.g., Committed Action), then bring it up with your therapist. They can help you explore what might be getting in the way and adjust your approach or focus areas to support your growth better. Remember, therapy is a collaborative process, so your input and feedback are key!